This document describes to move the Azure AD Connect database
from the local SQL Server Express server to a remote SQL Server.
About this scenario
Following is
some brief information about this scenario. In this scenario, Azure AD Connect
version (1.1.819.0) is installed on a single Windows Server 2016 domain
controller. It is using the built-in SQL Server 2012 Express Edition for its
database. The database will be moved to a SQL Server 2017 server.
Move the Azure AD Connect database
Use the
following steps to move the Azure AD Connect database to a remote SQL Server.
1.
On the Azure AD Connect server, go to Services and
stop the Microsoft Azure AD Sync service.
2.
Locate the %Program Files%\Microsoft Azure AD
Sync/Data/ folder and copy the ADSync.mdfand ADSync_log.ldf files
to the remote SQL Server.
3.
Restart the Microsoft Azure AD Sync service
on the Azure AD Connect server.
4.
Un-install Azure AD Connect by going to Control Panel - - Programs
- Programs and Features. Select Microsoft Azure AD Connect and click uninstall
at the top.
5.
On the remote SQL server, open SQL Server Management Studio.
6.
On Databases, right-click and select Attach.
7. On
the Attach
Databases screen, click Add and
navigate to the ADSync.mdf file. Click OK.
8.
Once the database is
attached, go back to the Azure AD Connect server and install Azure AD Connect.
9.
Once the MSI
installation completes, the Azure AD Connect wizard starts with the Express
mode setup. Close the screen by clicking the Exit icon.
10. Start a new command prompt or PowerShell session. Navigate to
folder \program
files\Microsoft Azure AD Connect. Run command .\AzureADConnect.exe
/useexistingdatabase to start the Azure AD Connect wizard in “Use existing
database” setup mode.
11. You are greeted with the Welcome to Azure AD Connect screen.
Once you agree to the license terms and privacy notice, click Continue.
12. On the Install
required components screen, the Use an
existing SQL Server option is enabled. Specify the name of the SQL server
that is hosting the ADSync database. If the SQL engine instance used to host
the ADSync database is not the default instance on the SQL server, you must
specify the SQL engine instance name. Further, if SQL browsing is not enabled,
you must also specify the SQL engine instance port number. For example:
13. On the Connect to
Azure AD screen, you
must provide the credentials of a global admin of your Azure AD directory. The
recommendation is to use an account in the default onmicrosoft.com domain. This
account is only used to create a service account in Azure AD and is not used
after the wizard has completed.
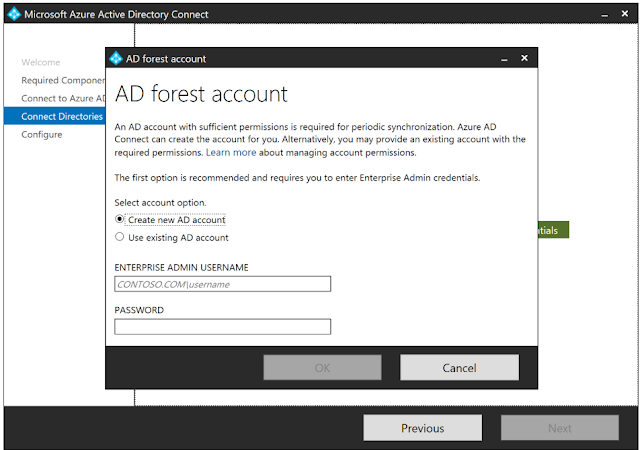
14. On the Connect
your directories screen, the existing AD forest configured for directory
synchronization is listed with a red cross icon beside it. To synchronize
changes from an on-premises AD forest, an AD DS account is required. The Azure
AD Connect wizard is unable to retrieve the credentials of the AD DS account
stored in the ADSync database because the credentials are encrypted and can
only be decrypted by the previous Azure AD Connect server. Click Change
Credentials to specify the AD DS account for the AD forest.
15. In the pop-up dialog, you can either (i) provide
an Enterprise Admin credential and let Azure AD Connect create the AD DS
account for you, or (ii) create the AD DS account yourself and provide its
credential to Azure AD Connect. Once you have selected an option and provide
the necessary credentials, click OK to close the
pop-up dialog.
16. Once the credentials are provided, the red cross
icon is replaced with a green tick icon. Click Next.
17. On the Ready to
configure screen, click Install.
18. Once installation completes, the Azure AD Connect server is
automatically enabled for Staging Mode. It is recommended that you review the
server configuration and pending exports for unexpected changes before
disabling Staging Mode